As part of its Evaluation of Approaches to Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Washington State, the Climate Legislative and Executive Workgroup (CLEW) has tasked Science Applications International Corporation (SAIC) with analyzing Washington State Emissions and Related Energy Consumption (Task 1), in several parts.
SAIC completed these tasks, with the following analysis of emissions, energy consumption, and energy expenditures in Washington from 1990 to 2011. This document provides an analysis of energy consumption and expenditures in Washington State and examines how energy consumption impacts GHG emissions.
Key Findings:
Emissions
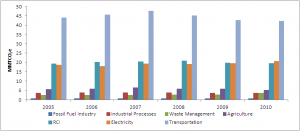
- The transportation sector is the largest source of emissions in Washington State. Within this sector, on-road gasoline consumption is the largest single source of emissions. Other important emission sources in the transportation sector are aviation fuels and diesel fuel.
- The electricity and residential, commercial, and industrial (RCI) sectors are the second largest emitting sectors, after transportation. In the electricity sector, coal consumption for electricity is the largest single source, while in the RCI sector, natural gas consumption is the largest source.
- Natural gas consumption is the largest source of emission in the RCI sector, primarily heating fuel for buildings, followed by oil, which is primary used in the industrial sector.
- Total emissions in the state have been declining since 2007. There was a small increase in emission in 2010, primarily due to increased fossil fuel electricity consumption in response to drought conditions that reduced hydroelectric power output. The only other sectors that showed increased emissions in 2010 were the industrial processes and waste management sectors.
Energy Consumption
- Washington consumed just over 1.5 quadrillion Btu of total energy in 2011.
- On a per capita basis, Washington consumed about 220 million Btu in 2011. Oregon and California consumed less energy per capita, at 193 and 201 million Btu per capita,
- respectively, in 2011. Idaho and Montana consumed more energy per capita, at 278 and 319 million Btu per capita, respectively, in 2011.
- In the transportation sector, Washington consumes less on-road transportation fuel (gasoline and diesel) per person than all other states in the region, except California. However, consumption of gasoline is still the largest source of emissions in the state.